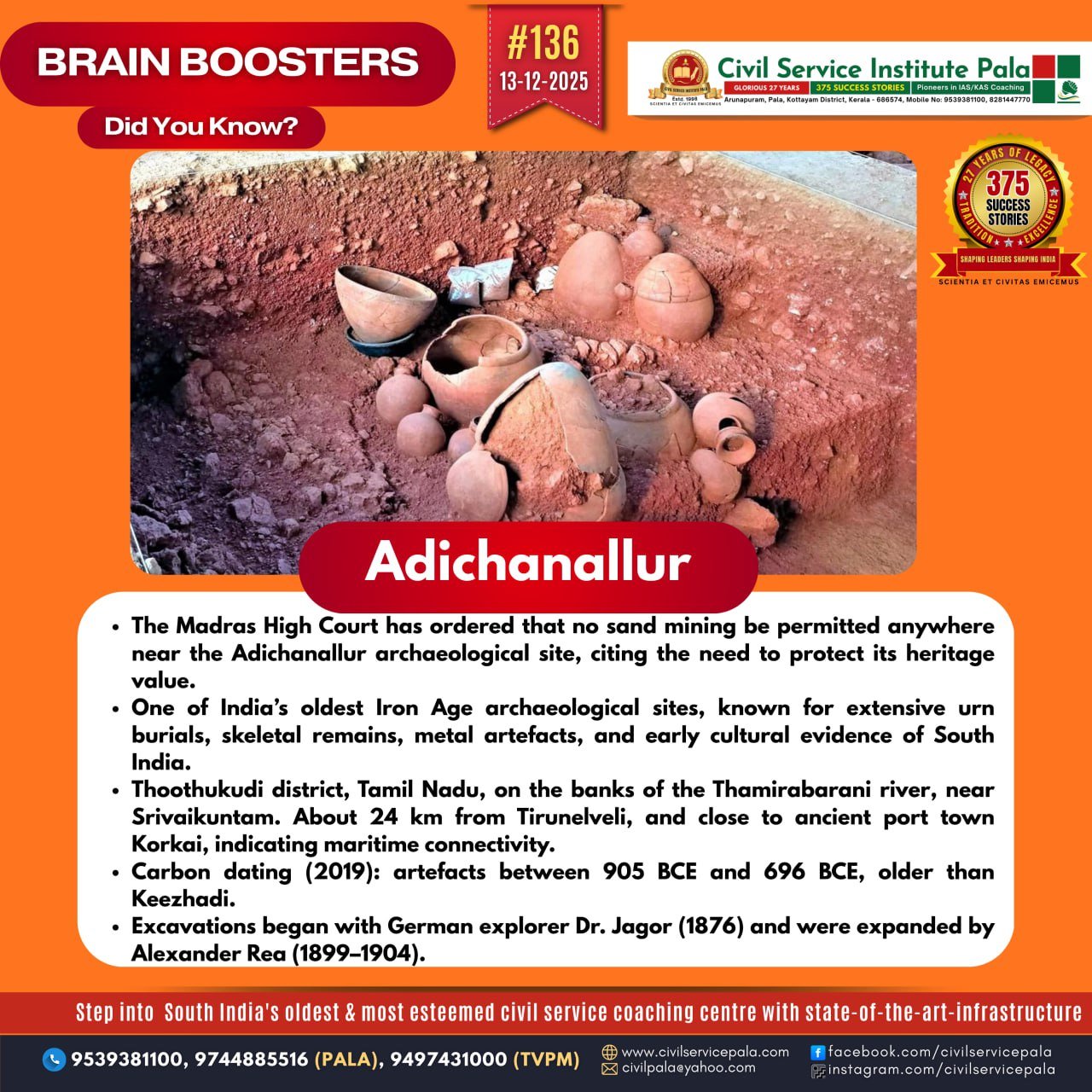
Adichanallur
Adichanallur is one of the most important prehistoric archaeological sites in India, shedding light on the early Iron Age and Megalithic culture of South India, particularly Tamil Nadu.
Location
Adichanallur is located in Thoothukudi (Tuticorin) district, Tamil Nadu, on the southern bank of the Tamiraparani River.
Its riverine setting indicates an advanced and settled ancient civilization.
Later excavations were carried out by the Archaeological Survey of India (ASI), notably during 2004–2005 and subsequent seasons.
Excavations revealed extensive burial urns, human skeletal remains, and cultural artefacts.
Cultural and Historical Significance
Adichanallur is associated with the Megalithic–Iron Age culture (c. 1000 BCE – 300 BCE).
The burial practices suggest belief in life after death, with grave goods placed alongside the dead.
Some findings indicate the presence of an even earlier advanced civilization, possibly predating the Sangam age.
Key Archaeological Findings
Large burial urns made of terracotta, often containing skeletal remains.
Iron tools and weapons such as knives, spears, and arrowheads.
Bronze and gold ornaments, including bangles and diadems.
Pottery with graffiti-like symbols, some resembling early Tamil-Brahmi scripts.
Evidence of social stratification, craftsmanship, and metallurgical knowledge.
Anthropological Importance
Skeletal remains show a mixed racial composition, suggesting interaction between different population groups.The findings challenge earlier assumptions about the antiquity and sophistication of South Indian civilizations.
Recent Developments
Scientific dating methods, including carbon dating, suggest habitation going back to over 3,000 years.
There have been efforts to declare Adichanallur a protected national monument and to establish a site museum.
Historical Importance
Adichanallur provides crucial evidence for:
The continuity of Tamil culture
Early urbanisation and metallurgy in South India
Advanced burial practices and social organization
Conclusion
Adichanallur stands as a landmark archaeological site that redefines the antiquity of Tamil civilization, offering invaluable insights into South India’s prehistoric past and strengthening the understanding of India’s early cultural evolution.
